Brazilian growers are significant adopters of agricultural biological products, such as biopesticides, biofertilizers, biostimulants and genetically modified (GM) crops. The reasons for this adoption are complex and multifaceted. Here are some insights into why agricultural biological products were more readily adopted in Brazil compared to other parts of the world:
1. Agricultural Practices and Climate
- Brazil has a tropical climate and extensive agricultural land, which makes it suitable for a wide range of crops in one season. This diversity created a need for various agricultural solutions, including biological products.
- Some biological products, such as certain biopesticides and biofertilizers, can be particularly effective in tropical and subtropical climates like those found in parts of Brazil.
2. Pest and Disease Pressure
- Brazil faces significant challenges with pest and disease pressure in its agricultural sector due to the hot and humid climate condition. Biological products, including biopesticides and beneficial insects, can offer sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives to chemical pesticides.
3. Environmental Regulations
- Brazil has had more strict regulations and environmental concerns regarding the use of chemical pesticides, which encouraged the adoption of more sustainable agricultural practices, including biological products.
4. Government Support
- Government policies and incentives, such as tax breaks and research funding, have been implemented to promote the adoption of biological products in Brazilian agriculture.
5. Research and Development
- Brazil has a strong agricultural research community that has focused on developing and promoting biological products. Institutions like Embrapa and universities have played a significant role in developing and disseminating these technologies.
6. Crop Diversity
- Brazil is a major producer of various crops, including soybeans, corn, sugarcane, cotton, rice, and coffee. The diversity of crops grown in Brazil led to a demand for tailored agricultural solutions, including genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
- Brazil’s agricultural evolution is propelled by several key factors. This encompasses significant advances in agricultural research that have led to enhanced crop yields, the expansion of available arable land, substantial investments in production technologies for diverse crop and forage varieties, and a notable upsurge in global demand for food and animal feed, notably within the last decade. Moreover, Brazil’s distinct advantage lies in its capacity to harvest two to three crops annually from the same land plot, which sets it apart from other grain and soybean-producing nations and positions it as a unique and competitive player in the global agricultural landscape.
7. Adoption of GM Crops
- Brazil has been one of the largest adopters of genetically modified (GM) crops, such as GM soybeans and GM maize (corn). These crops often incorporate traits that enhance resistance to pests and diseases, which reduces the need for chemical inputs.
8. Sustainability and Market Access
- Sustainable agricultural practices and products have gained importance in global markets. Brazilian farmers, looking to access international markets, have adopted more environmentally friendly practices, including biological products.
9. Knowledge Transfer
- Brazilian agricultural organizations and farmers have actively shared knowledge and experiences related to biological products, which has fostered their adoption and improved efficiency within the country.
10. Economic Factors
- Cost-effectiveness: Agricultural biological products can often be more cost-effective than traditional chemical inputs, especially in a country with a large agricultural sector like Brazil. They may require lower input costs and labor, which can be attractive to farmers looking to maximize profits.
- Access to raw materials: Brazil’s rich biodiversity provides a source of diverse microorganisms and natural compounds that can be used in biological products. This natural resource advantage can make it easier to develop and manufacture such products in the country.
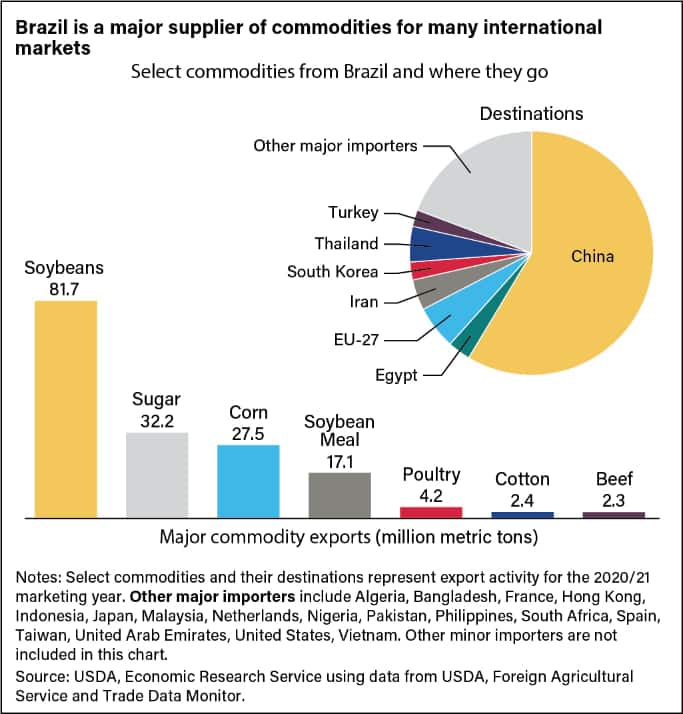
- Export opportunities: Brazil is a major exporter of agricultural products. The adoption of sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices, including the use of biological products, can improve the marketability of its exports.
It’s essential to keep in mind that the adoption of agricultural practices and technologies can be influenced by a wide range of factors, local factors, and the specific needs of different regions within Brazil can vary, which leads to variations in the adoption of biological products.
Brazil transformation
Brazil has undergone a transformation since the mid-2000s. It has shifted from being a primary exporter of tropical agricultural products like coffee, sugar, citrus, and cacao to becoming a major global supplier of a broader range of commodities, including soybeans, corn, cotton, ethanol, and meats. This transformation signifies Brazil’s expanding presence and contribution to global agriculture.
As a country with arguably the most arable land, Brazil has a significant amount of land suitable for farming and agriculture. It is also a top-5 producer of 34 different agricultural commodities, indicating the country’s diverse agricultural production capabilities. Furthermore, Brazil is the largest net exporter in agriculture, which showcases its global influence in agricultural trade.
To help you move your innovation to market, trust AgriThority® to be your native guides. With internationally recognized leaders connected to more than 400 local specialists in a worldwide network, we bring deep experience testing more than 539 technologies across 3500+ field trial locations for 275+ multi-national, mid-size and start-up companies.


